How British Exploring Society is Changing the Face of the Outdoor Charity Sector

Honor Wilson-Fletcher in front of young explorer artwork
Cambridge Management Consulting is proud to support the life-changing work accomplished by British Exploring Society. We interviewed Honor Wilson-Fletcher, CEO, about how the charity has stayed true to its roots but also reinvented itself to reach more young people
Connecting is at the heart of all we do: to be at one with the world around us and the people we share it with is at the centre of our daily lives.
No one knows this better than British Exploring Society, an incredible charity which sees outdoor education as the pathway to young people thriving. We are delighted to shine a light on the vital work which they are doing—as CEO Honor Wilson-Fletcher gives us an insight into what the past, present and future looks like for this very special organisation.
At its core, British Exploring Society is about celebrating young people and championing their potential. Yet, the way they approach this is unique and what truly provides such transformative results. By handing them the necessary skills and tools, young people are empowered and emboldened to take part in expeditions in all corners of the earth.
Young people who are underrepresented in outdoor education—those from ethnic minorities, economically disadvantaged communities or with physical impairment— are given the gift of independence, resilience and lasting memories which directly impact all aspects of their future. No teen or young adult pays to take part and all expeditions are now funded solely through kind donations. This is a transformative, once-in-a-lifetime experience which every young person deserves, and this charity is doing everything to make that possible.
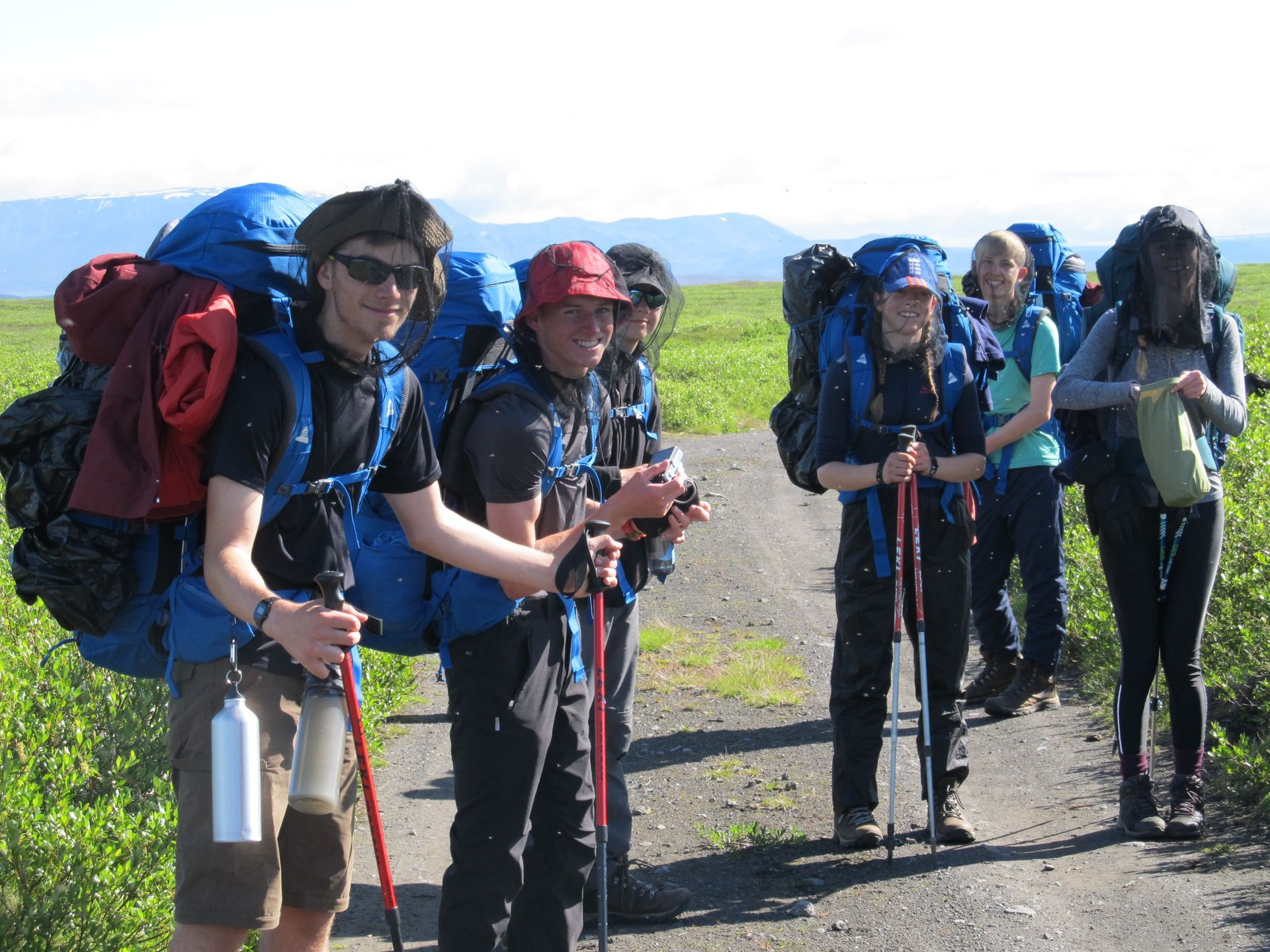

Young explorers on an expedition to Iceland
A Rich History of Exploration
Founded in 1932, British Exploring Society was the passion project of Surgeon Commander George Murray Levick RN, inspired by his expedition of 1910-13 to the Antarctic with none other than Captain Scott. Having completed the endurance battle to trump all, he wanted to bring back its transformative capabilities and extract his experience into something everyone could access. He did this at a time when nobody had conceived of anything like this, and he truly pioneered the model.
How can this past be found in the charity today? How does the organisation wear its military history? Honor admits that “We are proud of our history and our heritage, but hopefully not a victim of it. Murray Levick was a doctor, and he was our founder. Actually, finding leaders for the expeditions outside of the military was almost impossible during his time, because they were the only ones who had the training or experience needed. So, some of the language and the methodology, certainly in earlier years, came from the military because that was the only source that there really was.
“And even lots of things like the scouts and girl guiding was informed by a quasi-military background. Nowadays, some of the bits of training that we value such as jungle training still only the armed forces do. There are lots of sorts of technical tickets for mountaineering etc, but if you want that training, you have to go to someone who has been in the armed forces. And some of our best leaders come from the uniformed professions generally, like community police officers who make incredible youth leaders. Uniformed professions, which have a sort of commitment to community, are generally something which fits really well with our ethos. We would be nothing without the members of our community go on all our expeditions. We are a community as much as we are an organisation.”
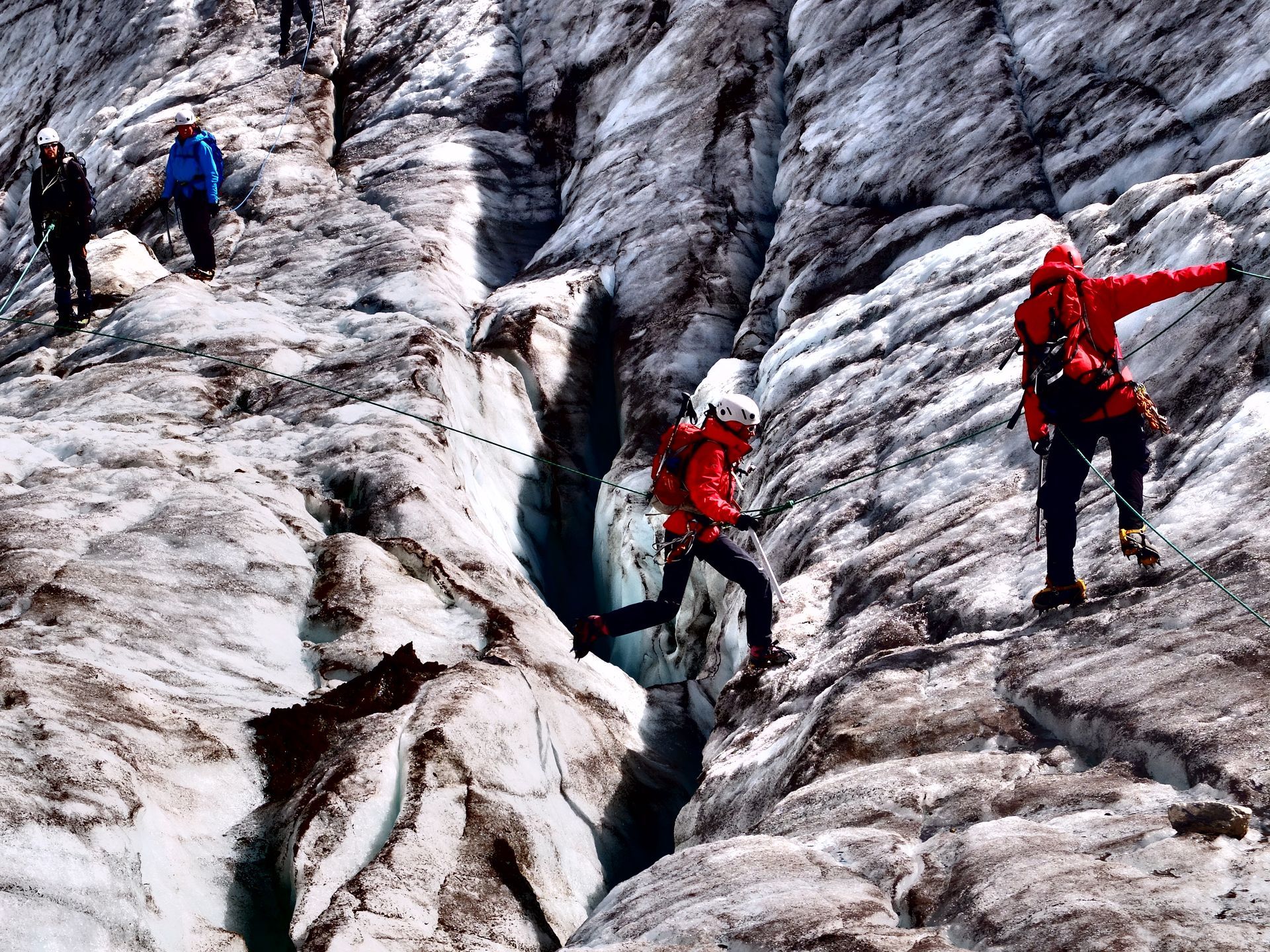

A group of explorers learn how to stay safe when climbing difficult terrain
A New Direction for the Charity
Much of this exciting change can be credited to CEO Honor Wilson-Fletcher, who took over the helm in February 2016. When asked what drove her to the project, she announced that she “was initially thinking of taking a break over the summer and then some friends saw this opportunity advertised and knew that it had my name written all over it. I was a bit worried as it looked like it was very patriarchal, had a lengthy military history and used to be called Public Schools Exploring Society. But, I was also very intrigued, and it sounded like its core was really interesting. At its heart, it was so ambitious and what the team wanted to do was make it more accessible to young people who had had a tough start in life. And amazingly, six and a half years ago they took me on. We’ve completely changed the operating model but have still got loads to do, which excites and challenges me daily.”
With a history in publishing, this move to the charity sector was surprising to many, including Honor herself: “My first role was amazingly at the British Museum. They took me on, and it was an unbelievable culture shock. It is an enormous organisation and all the decision-making happens where you least expect it. Decisions are not made in meetings; it’s all done through inference and everyone’s timescales are so different. Archaeologists can wait 30 years for a decision. I was so used to everything being a single line and I learnt so much about holding on to the endgame whilst navigating really complex groups of stakeholders.“
The Future of Outdoor Education
Although British Exploring Society is all about leaving its mark and creating lasting impact, there remains one area of the organisation where Honor is passionate about leaving no tracks. As a charity whose work is so intensely linked with the natural world, recognising its fragility and treating it with respect is part of what makes their work so important. To spend time among magical landscapes and truly appreciate the impact we have on them is vital. This project is so far away from being superficial: it is transformative in terms of character but also in terms of perspective. It is the environment which pushes these young adventurers and allows them to thrive. To not return the gift would be just another abuse.
As a result, Honor is dedicated to radically reducing the carbon footprint of the charity and crafting an organisation that will work with the earth, not against it. Despite already taking positive and decisive action to limit their carbon output, Honor explained how her team continue to look forward. Consulting an external team of specialists to plan concrete steps towards progress, they want to go beyond carbon neutral and truly embed the process of ethical offsetting programmes into their DNA.
As an organisation whose model is based on travel and exploration, this is no light statement. But with the help of technology and a constant re-calibrating between goal and actions, they are certain they will achieve it.
British Exploring Society is ambitious and excited about embracing the future. Despite its rich history, Honor is adamant that this organisation does not become stuck there. It is charging forward.
The organisation’s drive for change does not stop here. They are passionate about making the outdoors accessible to all young people, regardless of their socio-economic environment. Going on expeditions to far-flung places is not something within reach for many children in the UK. A big part of the mission is to help young people see themselves going to places where they have not traditionally been able to go. This preparation takes the form of school workshops, which condense the benefits and the experience of an expedition for young children, planting the seed that the outdoors and its effects are achievable.
Yet, Honor is aware that some of the limits and inequality are out of her control, and this goes for their instructors as well as the young people they support. Honor notes that ”you can only really pursue a career in the outdoors if you have a safety net at the moment and for a lot of people, that just isn’t an option. As a result, there must be structural changes which are beyond us.” However, she hopes “that we can support individuals who can make that decision themselves or support young people who are on that journey.
“We also have to support other organisations doing great work like Muslim Hikers and Black Girls Hike and many others who we are trying to learn from without making them responsible for all of the insight in the world. We have to be working with people who are doing great work that we may never be able to do. They provide an environment that makes Muslim women feel incredibly safe in a way that we would really struggle to match. So, some of it is about partnership and also advocacy. We have to be doing as well as saying if we want to see that change.”
This is where Honor’s wealth of experience comes in. Having previously acted as CEO for 6 years at the Aldrige Foundation, which successfully established 12 state schools in some of the most deprived parts of England, she has always been passionate about changing the lives of young people. British Exploring Society is no different.
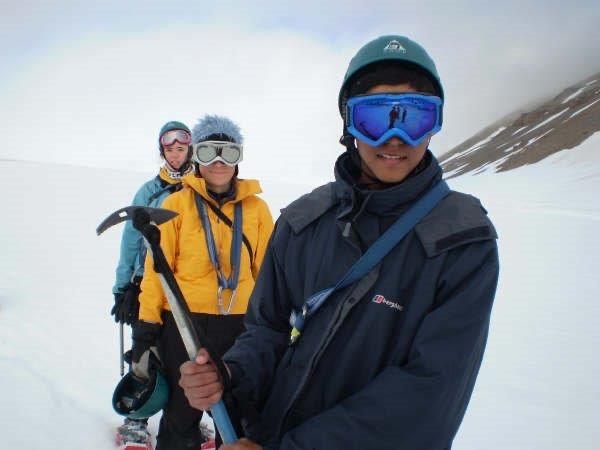

A group on a polar expedition learn about tools and hiking in snow

As British Exploring Society approaches its 100th birthday, the charity asks itself the same questions we all do when blowing out our candles: who are we and what do we want to do? Honor and her team embrace the past and the present with one mission: to reach more young people and transform their lives. We know that this reach will only grow, and the world can only be a better place because of that.
Cambridge Management Consulting is very proud to support the life-changing work accomplished by British Exploring Society. As an organisation, we are closely connected to the outdoors in more ways than one. Our founder and chairman, Tim Passingham, is a patron for the charity, and like all of the team, is dedicated to supporting environmental causes as well as other charities connected to the welfare of children and young adults. We give 1% of our time and profits to charities and non-profits who are doing incredible work in the third sector.
To find out more about the incredible work done by British Exploring Society, head over to their website:
https://www.britishexploring.org/
Why We Go Where We Go
Cambridge Management Consulting worked with British Exploring Society to create a video to answer the question 'Why We Go Where We Go'. They take young people to some of the most alien and remote locations around the world as part of a transformative model that combines real-world challenges with personal development and the awe of wilderness. The locations are an essential element in the success of this model.
You Can Help British Exploring Society
If you would like to support British Exploring Society with a monthly or annual donation; or would like to know more ways you can help their amazing work, please go to their donations page: https://www.britishexploring.org/support-us/donate/
Contact - Africa
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Blog Subscribe
SHARE CONTENT